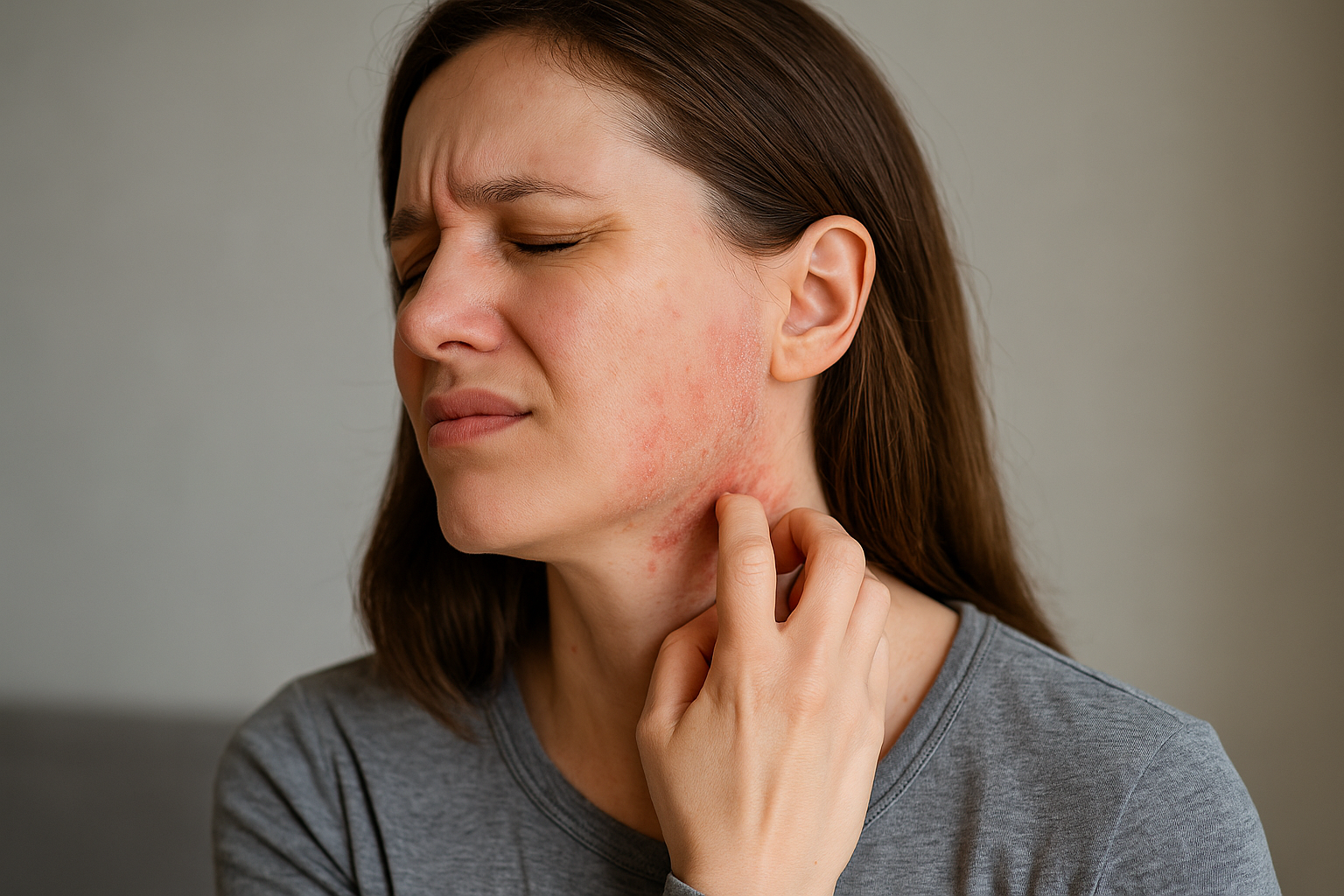
Eczema, medically known as atopic dermatitis, is a complex inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of adults across the globe. While often perceived as a childhood issue, eczema can persist or even begin during adulthood, especially under the influence of modern environmental and lifestyle factors. Flare-ups can be both physically painful and emotionally distressing, disrupting daily activities, self-confidence, and sleep quality. The key to minimizing the impact of eczema lies in understanding what fuels these flare-ups.
This expanded expert guide dives deep into the most common—and some surprising—eczema triggers in adults. You’ll also find detailed strategies for identifying, managing, and preventing future flare-ups using an integrative and evidence-based approach.
💡 What Triggers Eczema Flare-Ups in Adults?
Adult eczema flare-ups can be triggered by irritants such as harsh soaps, allergens, stress, climate changes, food sensitivities, hormonal shifts, and even certain medications. Identifying and managing these triggers is essential to maintaining clear and healthy skin.
Who Should Read This?
This guide is especially useful for:
- Adults aged 25–65 living with chronic or recurring eczema
- People recently diagnosed with adult-onset eczema
- Wellness enthusiasts seeking natural relief
- Skincare-conscious individuals experimenting with routines and products
- Busy professionals and caregivers struggling with environmental stressors
Understanding Adult-Onset Eczema
Adult eczema can be driven by:
- A weakened skin barrier function
- Overactive immune responses
- Environmental pollutants
- Hormonal changes (especially during perimenopause)
It often appears as:
- Dry, scaly, or leathery patches
- Swollen or inflamed skin
- Cracks, bleeding, or oozing
- Intense itching, often worse at night
Eczema tends to flare cyclically, worsening with exposure to specific triggers.
18 Eczema Triggers to Watch Out For
1. Harsh Soaps, Detergents, and Surfactants
Many commercial soaps and body washes contain sulfates, parabens, and alcohols that strip away natural oils.
2. Environmental Stressors
Air pollution, smog, and cigarette smoke can inflame the skin and worsen eczema.
3. Emotional Stress and Anxiety
Stress increases cortisol, which compromises the skin barrier and triggers inflammation.
4. Rapid Climate Changes
Switching between air-conditioned rooms and outdoor humidity stresses sensitive skin.
5. Pollen, Mold, and Dust Mites
Environmental allergens are often invisible but highly reactive.
6. Sweat and Body Heat
Sweat contains salts and acids that irritate eczema-prone areas, especially under clothing.
7. Wool, Polyester, and Synthetic Fabrics
These fabrics cause friction and prevent breathability, aggravating eczema patches.
8. Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Common offenders: dairy, gluten, eggs, soy, shellfish, and nightshades.
9. Fragrances in Lotions, Shampoos, and Detergents
Even “natural” products may include essential oils or botanical extracts that cause irritation.
10. Tap Water High in Chlorine or Minerals
Hard water with calcium or magnesium can dry out skin; chlorine can exacerbate irritation.
11. Alcohol and Caffeinated Beverages
These dehydrate the skin and can worsen inflammation in sensitive individuals.
12. Hormonal Shifts
Menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause can alter skin sensitivity and barrier function.
13. Overwashing or Exfoliating Too Often
Removing too much oil from the skin barrier can result in flare-ups and stinging.
14. Certain Medications
NSAIDs, antibiotics, or retinoids can provoke eczema as a side effect.
15. Latex and Rubber Products
Gloves, bands, and adhesives may contain allergens triggering contact dermatitis.
16. Animal Dander
Cats, dogs, and even birds can shed proteins that inflame sensitive skin.
17. Sunburn and UV Overexposure
Although some sun can help, overexposure damages skin and delays healing.
18. Tight Clothing and Accessories
Pressure from straps, waistbands, and collars may create friction-induced eczema.
How to Identify and Track Your Triggers
- Start a digital or written eczema diary
- Note time, location, weather, products used, and foods eaten
- Use elimination methods under supervision
- Consider patch testing with a dermatologist
- Get tested for IgE allergies and food intolerances
Pro Tips from Dermatologists and Experts
- Layer moisturizers: Use a ceramide-rich cream, then seal with an ointment.
- Use a humidifier at night to protect skin during dry seasons.
- Apply cold compresses to stop itching before scratching starts.
- Wear loose-fitting cotton clothing to minimize friction and overheating.
- Keep nails short and clean to prevent skin infections from scratching.
- Schedule routine checkups to monitor skin, allergy, and gut health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can eczema get worse with age?
Yes. Without proper care and avoidance of triggers, adult eczema can become more chronic and widespread.
Are topical steroids safe?
Short-term use can be effective. Long-term use should be monitored due to the risk of thinning skin or rebound flares.
Is eczema related to gut health?
Yes. Studies link eczema with gut dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”).
Can probiotics help?
Probiotic strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus may improve skin resilience and reduce inflammation in some individuals.
Are there eczema-friendly diets?
Elimination diets and anti-inflammatory protocols like the AIP (Autoimmune Protocol) or low-histamine diet have shown benefits.
Your Turn: What Triggers Your Eczema?
Have you identified your biggest triggers yet?
👇 Share your story, ask questions, or leave tips for others managing adult eczema.