Understanding the Thyroid Gland and Its Role
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck. Though small, it plays a big role in your body’s metabolism, growth, and development by releasing hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate heart rate, body temperature, and even how quickly your body uses energy.
When something goes wrong with the thyroid, especially when cancer develops, these functions can be disrupted. Thyroid cancer, while relatively rare compared to other cancers, is becoming more common — especially among women and those exposed to certain risk factors.
What Is Thyroid Cancer?
Thyroid cancer occurs when cells in the thyroid grow uncontrollably. There are several types:
-
Papillary thyroid cancer: Most common and often grows slowly.
-
Follicular thyroid cancer: Second most common; may spread to lungs or bones.
-
Medullary thyroid cancer: Rarer and may be inherited.
-
Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Aggressive and harder to treat.
Most thyroid cancers grow slowly and are highly treatable when caught early — but that’s why recognizing the signs is so crucial.
Early Warning Signs of Thyroid Cancer
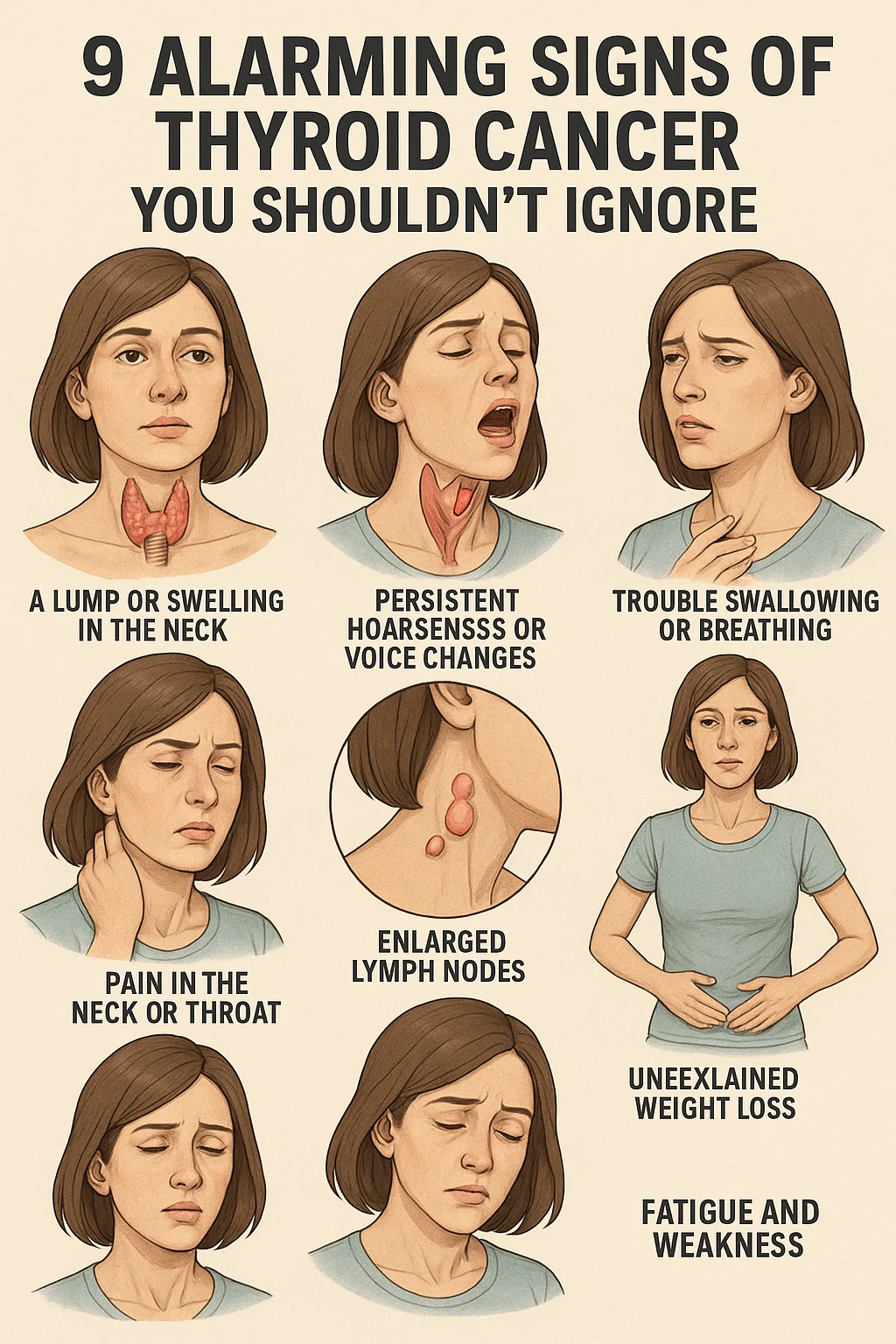
A Lump or Swelling in the Neck
The most common early sign of thyroid cancer is a lump or nodule in the neck. While many thyroid nodules are benign, some can be cancerous. You might feel it yourself or notice it in a mirror, especially if it moves when you swallow.
Persistent Hoarseness or Voice Changes
If a tumor affects the vocal cords or nearby nerves, your voice may sound hoarse or raspy for an extended period without a clear reason, such as a cold or overuse.
Trouble Swallowing or Breathing
A growing mass in your neck can compress the windpipe or esophagus, making it difficult to breathe or swallow. This can feel like constant pressure in the throat.
Pain in the Neck or Throat
Some people experience persistent pain in the front of the neck or radiating up to the ears. If the pain doesn’t go away, it’s worth getting checked out.
Advanced Symptoms to Watch Out For
Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck can signal that thyroid cancer has spread beyond the gland itself. These may feel firm and painless.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Thyroid hormones play a key role in regulating metabolism. A sudden drop in weight, especially without diet or exercise changes, may be a red flag.
Fatigue and Weakness
Persistent tiredness, especially when paired with other symptoms, can be a sign that the cancer is affecting your body’s normal functions.
Risk Factors and Causes of Thyroid Cancer
Several factors can increase your risk:
-
Gender: Women are three times more likely to develop it.
-
Age: Most cases occur between ages 30 and 60.
-
Radiation exposure: Especially during childhood.
-
Family history: Medullary thyroid cancer can be inherited.
-
Iodine deficiency: Though rare in developed countries, it remains a risk.
When to See a Doctor
Don’t ignore a persistent lump in your neck or voice changes. See a doctor if symptoms last more than a couple of weeks, or if you have risk factors. Early diagnosis makes a big difference.
How Thyroid Cancer Is Diagnosed
-
Ultrasound: Helps determine the size and nature of the nodule.
-
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: Extracts tissue for lab analysis.
-
Blood tests: May include thyroid function tests and calcitonin levels.
-
CT or MRI scans: Used in certain cases for staging.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Cancer
Treatment depends on the type and stage:
-
Surgery (thyroidectomy): Removal of all or part of the thyroid.
-
Radioactive iodine therapy: Destroys remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
-
Thyroid hormone therapy: Helps replace hormone function and suppress recurrence.
-
External beam radiation or chemotherapy: For more aggressive types.
Living with and Beyond Thyroid Cancer
Life after treatment often includes:
-
Daily thyroid hormone pills
-
Regular follow-ups and blood tests
-
Monitoring for recurrence
-
Emotional and physical adjustment
With timely treatment, most people with thyroid cancer lead full, healthy lives.
Preventive Measures and Screening
While there’s no surefire way to prevent thyroid cancer, you can:
-
Avoid unnecessary radiation exposure
-
Monitor any thyroid nodules
-
Know your family history
-
Get regular checkups if you’re at risk
FAQs About Signs of Thyroid Cancer
Q1: Are thyroid nodules always cancerous?
No, over 90% of thyroid nodules are benign, but they should be evaluated.
Q2: Can thyroid cancer be detected through a blood test?
Blood tests can support diagnosis but usually aren’t definitive alone.
Q3: How fast does thyroid cancer grow?
Papillary thyroid cancer grows slowly, while anaplastic can be aggressive.
Q4: Does thyroid cancer cause weight gain or loss?
Weight loss is more common, especially with hormonal imbalances.
Q5: Is thyroid cancer painful?
Not usually in early stages, but pain may develop if the tumor grows.
Q6: What age group is most affected?
People between 30–60 years, especially women.
Conclusion: Know the Signs, Act Early
Recognizing the signs of thyroid cancer can truly save lives. The earlier it’s caught, the better the outcome. If you notice any of the warning signs — a lump, voice change, or difficulty swallowing — don’t hesitate to seek medical attention.